| 1. Project Risk Management includes all of the following processes except: |
|---|
| 2. Using the PMBOK definition of contingency reserve, which of the following statements about contingency reserves is false? |
|
|
| 3. Which of the following is not a tool or technique used during the Risk Quantification Process? |
|
|
| 4. Which of the following is true about pure risk? |
|
|
| 5. A contingency plan is |
|
|
| 6. The normal risk of doing business that carries opportunities for both gain and loss is called: |
|
|
| 7. A risk response which involves eliminating a threat is called: |
|
|
| 8. Deflection or transfer of a risk to another party is part of which of the following risk response categories? |
|
|
| 9. When should risk identification be performed? (select best answer) |
|
|
| 10. Which of the following statements is false? |
|
|
| 11. A contingency plan is executed when: |
|
|
| 12. Management reserves are used to handle which type of risk? |
|
|
| 13. Which of the following techniques accounts for path convergence and generally estimates project durations more accurately? |
|
|
| 14. Most schedule simulations are based on some form of which of the following? |
|
|
| 15. When should a risk be avoided? |
|
|
| 16. If a project has an 80% chance of having the scope defined by a certain date and a 70% chance of obtaining approval for the scope by a certain date, what is the probability of both events occurring? |
|
|
| 17. The independence of two events in which the occurrence of one is not related to the occurrence of the other is called: |
|
|
| 18. The one document that should always be used to help identify risk is the: |
|
|
| 19. Risks are accepted when: |
|
|
| 20. An example of risk mitigation is: |
|
|
| 21. A process that is not part of Project Risk Management is |
|
|
| 22. A response to negative risk event is known as a: |
|
|
| 23. Who is responsible for risk identification, risk quantification, risk response development, risk response control? |
|
|
| 24. In summing probability distributions what is the formula for Mean? |
|
|
| 25. In beta distributions using PERT approximations what is the formula for Variance? |
|
|
| 26. When summing the probability distributions if the distributions are skewed to the __________, the project mean will always be significantly higher than the sum of the most likely estimates. |
|
|
| 27. By using Project Risk Management techniques project managers can develop strategies that do all but which of the following: |
|
|
| 28. Which phase of the project life cycle typically has the highest uncertainty and risk associated with it? |
|
|
| 29. Risks classified as unknown (i.e., those which cannot be identified or evaluated): |
|
|
| 30. Risks can be divided into two basic types: business risk and pure (or insurable risk). Of the following, which one(s) fall(s) under business risk? |
|
|
| 31. The type of contract (payment mechanism) chosen for a project is of the degree of risk associated with completing that project. For a firm fixed price contract, payment for risks: |
|
|
| 32. The principles of risk management should be followed only for: |
|
|
| 33. Deflection involves the transfer of risk by such means as: |
|
|
| 34. Risk mitigation involves all but which of the following: |
|
|
| 35. Total Project Risk |
|
|
| 36. In Project Risk Management, Risk Response may include actions to: |
|
|
| 37. “Fast Tracked” project awarded and begun before all planning and risk assessment information is complete and available: |
|
|
| 38. Risk event probability is determined as: |
|
|
| 39. Final risk quantification and modeling normally considers the impacts of all risks combined and: |
|
|
| 40. Sensitivity Analysis can be used in risk analysis to: |
|
|
| 41. Many companies self-insure against some risks. Problems which can arise from self-insurance include |
|
|
42. Using the figure below, what is the probability of success for project B?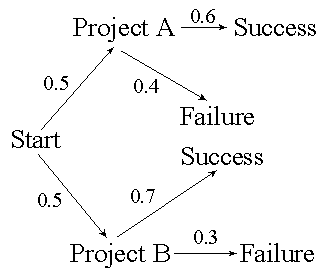 |
|
|
| 43. In performing an impact analysis the most effective tool to ensure all risks are identified on large projects is the: |
|
|
| 44. Budgeted contingencies can be determined by: |
|
|
| 45. During which phase of the project life cycle is the amount at stake lowest? |
|
|
| 46. Contingent planning should include all but which of the following? |
|
|
| 47. Critical variance is best described as |
|
|
| 48. The Delphi method involves brainstorming as a method of risk identification. |
|
|
| 49. Your manager has told you that you have a 10% chance of getting a “1” appraisal and an 80% chance of getting a “2” appraisal. What are you chances of getting a “3” appraisal? |
|
|
| 50. The single point standard deviations are 3, 5, 10, and 3 for the critical path. What is the standard deviation for the entire path? |
|
|
| 51. Mitigating risk could involve |
|
|
| 52. The 200 million dollar nuclear power plant you have just built cannot be activated because a pair of rare spotted owls have just built their nest in your steam tower. You explain this to the CEO of the utility as |
|
|
| 53. A manager who says “I’ll pay for it, but I want it as soon as possible” is considered to be |
|
|
| 54. If the mean is 3, the mode is 4, the median is 2, the PERT is 6, and one standard deviation is 3, a 95% confidence level is between |
|
|
| 55. Final risk quantification and modeling normally considers the impacts of all risks except possibly those due to |
|
|
| 56. Risk management is defined as the art and science of _________ risk factors throughout the life cycle of a project. |
|
|
| 57. Project risk is defined as the cumulative effect of the chances of _________ that will adversely affect project objectives. |
|
|
| 58. The three factors that characterize project risk are _________. |
|
|
| 59. Risk event is the precise description of what might happen to the _________ of the project. |
|
|
| 60. In the risk management context, mitigation and deflection are moth means of _________ the risk to the _________ objectives. |
|
|
| 61. Contingency planning is a means to _________ risks to the project through a formal process and provide the resources to meet the risk events. |
|
|
| 62. Suppose a project manager is negotiating with a subcontractor to provide the installation and integration of a computer system with data links. The data links must access three different computer protocols and provide a common data communication. This integration of the data protocols has never been accomplished. Since both are attempting to avoid any risk, the project manager would like to a award a _________ contract, while the subcontractor would like to sign only a _________ contract. |
|
|
| 63. Suppose a project manager of a research and development contract is charged with building a new radar antenna for an aircraft. The weight is limited to 12 pounds in the specification. This represents a major weight reduction over current systems, which weigh in excess of 26 pounds. Before starting the project, the project manager should __________. |
|
|
| 64. Suppose the project manager is evaluating the bids of two vendors. Each vendor offers to sell similar electronic components, which are integrated at the vendors site. To avoid the most risk, the project manager views items such as the vendor’s __________. |
|
|
65. Suppose the project manager must submit a summary risk assessment to the director of project managers. The assessment is to be made for each component of a new electronics system. The project manager submits the following:
The problem with the project manager’s risk assessment is that __________. |
|
|
| 66. Suppose the project is set at $2,300,000 for the total project. Some work that must be accomplished has not been identified in the initial planning. The most appropriate source of funds to cover this work is the __________. |
|
|
| 67. Suppose the project manager is planning courses of action to develop the strategy for the project. Courses “A” and “B” are both feasible options and can be implemented. Senior management has directed that risk be considered, but there is a need to maximize the profit on this project. A decision tree is used as a valid means for selecting the most profitable option. Course “A” has a potential profit of $27,500 with a probability of 0.75 success. Course “B” has a potential profit of $20,800 with a probability of 0.90 success. The course of action that should be selected is __________. |
|
|
| 68. Suppose the project has many hazards that could easily injure one or more persons and there is no method of avoiding the potential for damages. The project manager should consider __________ as a means of deflecting the risk. |
|
|
| 69. The primary characteristic that distinguishes external and internal risk areas is the __________. |
|
|
| 70. There are two general categories of risk areas, internal and external. Examples of external risk areas are __________. |
|
|
| 71. In the area of legal risks, there are two reasons for licensing of projects. One reason is for revenue generation by the community, while the other is for __________. |
|
|
| 72. Intellectual property rights assigned to an individual by means of a patent or copyright have value to the owner. Any infringement on those rights during the implementation of a project can __________. |
|
|
| 73. During the conduct of impact analysis for any risk, the individual performs screening. Screening is for the purpose of determining whether the risk is __________ the project. |
|
|
| 74. Suppose a project of $1.5 million has an adverse event that has a probability of 0.07 of occurrence and a potential loss of $15,000. This represents an expected negative value of __________. |
|
|
| 75. The assigned values of risk for a project is best accomplished through a structured methodology that ensures all project elements are evaluated. The project tool that is best suited for the structured analysis of the project risk is the __________. |
|
|
| 76. During the assessment of the risk to attempt to quantify the probability of failure and the amount of potential loss, the project manager uses the __________ personnel to make the estimates. |
|
|
| 77. Suppose during the risk analysis process that one identified risk event cannot be avoided, mitigated, or insured. The risk event is a critical item that, if it occurs, could cause the project to fail. the best option for the project manager is to __________. |
|
|
| 78. Suppose during project implementation on a fixed price contract, the budget for one work package has cost more than estimated because of an error that required reworking the task. The cost of materials and labor to rework the task required is $3,117 more than the budget. The money for this rework is covered by the __________. |
|
|
| 79. The PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) is a method of scheduling projects. In the context of risk, PERT is better than CPM (Critical Path Method) because it deals with the __________. |
|
|
| 80. Suppose the project manager establishes a risk model that will be used on the CALTRON Project. The risk model identifies the risk events and assigns probabilities of occurrence. However, what is missing from the risk model is __________. |
|
|
| 81. A high-risk project usually receives the highest priority by the top management. To effectively manage the project, the project manager should establish with the top management a charter that calls for his __________ and the basis for __________ without prior consultation. |
|
|
| 82. High-risk projects are always of concern to senior management and will receive the most scrutiny. The major concern of the project manager of a high-risk project is the tendency for senior management to often __________. |
|
|
| 83. Risk may be transferred from the owner (buyer) to the contractor (seller) through a contractual vehicle. the risk transfer is usually accomplished by the owner awarding a fixed price contract where the contractor agrees to perform for a single price. For the owner this simple solution has hidden costs that include all but __________. |
|
|
| 84. Guarantees in a project agreement give some degree of assurance to the owner (buyer) that the end product will meet the specified requirements, but they also represent potential future costs to the contractor (seller), or cost risk, if the system fails. The four express (as compared to implied) guarantee categories are __________. |
|
|
| 85. A project may have an implied warranty that is not specifically detailed in the contract. This implied warranty represents potential future costs for failure to meet the requirements and is a risk to the project. Implied warranties are usually those associated with __________, which are spelled out in the Uniform Commercial Code. |
|
|
| 86. Performance of a contract can bring liabilities that have implications of risk but are perhaps not as visible as the stated and implied warranty and guarantee. Two of these liabilities are __________ infringements. |
|
|
| 87. Project risk through liability comes in two forms: breach of contract and a tort. Breach of contract is essentially a failure to perform the service or provide the required product, while a tort is a personal wrong such as __________. |
|
|
| 88. Risk of loss may be transferred to an insurance underwriter by means of an insurance policy. Such policies state the monetary value of property damage that will be given for sustained losses. To make an informed decision about buying insurance, the project manager needs to determine the ratio of insurance cost and the expected value of the loss. for example, if the cost of insurance is $10,000, the value of the property is $200,000, and the probability of loss is 0.05 ( or five percent), the insurance is __________. |
|
|
| 89. Lease, rental, and hire of equipment for short periods of time to perform specified project work is a common practice. The equipment poses __________ unless the contractor (lessor) __________. |
|
|
| 90. The owner (buyer) of a project usually has the right to direct changes to the scope of work while the project work is being accomplished. Often, the owner will orally request a change and insist that the change be initiated immediately without the normal documentation (e.g., a change order). When the change is initiated without documentation, __________. |
|
|
| 91. The probability of failure for a project element is often called exposure to risk, or risk exposure. This exposure may be mitigated by taking measures to avoid a particular approach or use of specific technologies. When the risk exposure cannot be reduced through selection of another alternative, the project manager should __________. |
|
|
| 92. Project risk should be identified and assessed prior to project initiation during the planning phase. Once the implementation starts, there is less time to objectively assess risk and select the more attractive alternatives. During the implementation there may be indications of risk (i.e., failure to meet the project’s objectives) such as __________. |
|
|
| 93. The project manager may realize that some terms of the contract and project objectives will not be met. It would be costly and time consuming to meet some specifications. The project has a high degree of exposure to risk at this point. Negotiation with the customer to reduce the risk exposure is a means that __________. |
|
|
| 94. Demonstration and performance tests are used to prove the functional and operating characteristics of a deliverable to the customer. The tests pose a risk when the __________ criteria are selected to demonstrate the capabilities because __________. |
|
|
| 95. Uncertainty is often used in conjunction with the term risk, implying that uncertainty is risk. Uncertainty is an unknown situation that may result from a lack of information to sufficiently quantify the probability of occurrence of an event and to determine the most likely outcome. Therefore, any uncertainty that has a potential for a major impact on a project should be __________. |
|
|
Delivering a high-quality product at a reasonable price is not enough anymore.
That’s why we have developed 5 beneficial guarantees that will make your experience with our service enjoyable, easy, and safe.
You have to be 100% sure of the quality of your product to give a money-back guarantee. This describes us perfectly. Make sure that this guarantee is totally transparent.
Read moreEach paper is composed from scratch, according to your instructions. It is then checked by our plagiarism-detection software. There is no gap where plagiarism could squeeze in.
Read moreThanks to our free revisions, there is no way for you to be unsatisfied. We will work on your paper until you are completely happy with the result.
Read moreYour email is safe, as we store it according to international data protection rules. Your bank details are secure, as we use only reliable payment systems.
Read moreBy sending us your money, you buy the service we provide. Check out our terms and conditions if you prefer business talks to be laid out in official language.
Read more